MRIT (Modified Retinacular Imbrication Technique or Lateral Fabellar suture) - One or more bands of monofilament nylon are placed around the stifle joint to restore stability.
MRIT Procedure
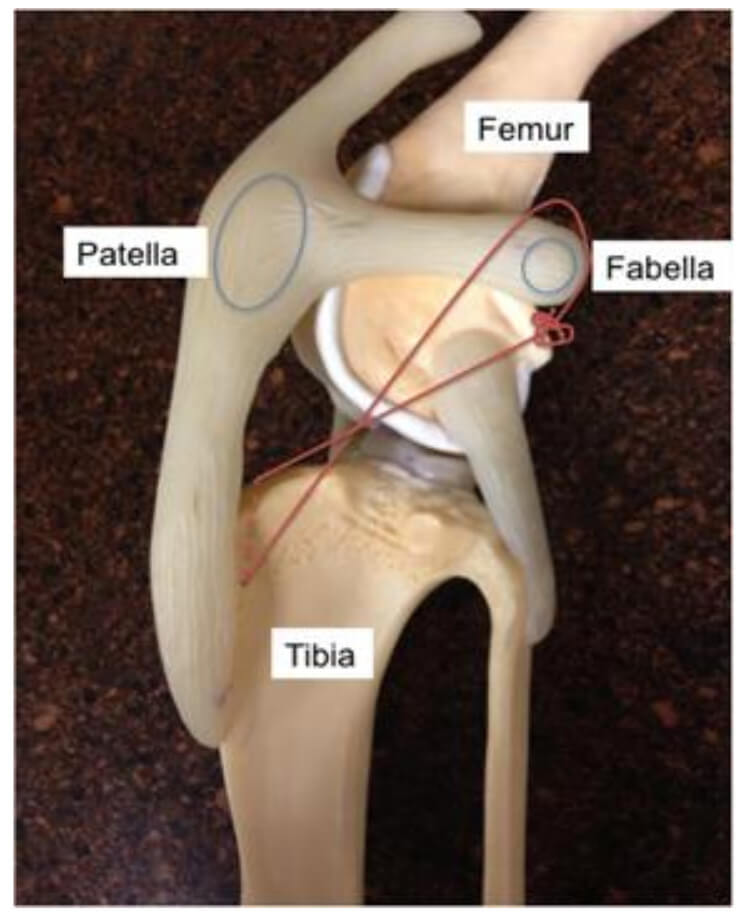 The MRIT procedure involves an incision over the inside or outside aspect of the knee (surgeon dependent). The joint is explored (arthrotomy) to examine the CCL, assess arthritis, and look for any meniscal injury. If there is a meniscal injury, the meniscus is partially removed. An intact meniscus may also be surgically “released” as a prophylactic measure against future injury (surgeon dependent). Next, a sterile suture is selected depending on the size, age, and activity level of the patient. The suture is passed around the fabella and through a tunnel created in the tibia. The suture is then tightened to stabilize the knee. See figure below. For larger patients, a suture can be placed on both the medial and lateral aspect of the knee.
The MRIT procedure involves an incision over the inside or outside aspect of the knee (surgeon dependent). The joint is explored (arthrotomy) to examine the CCL, assess arthritis, and look for any meniscal injury. If there is a meniscal injury, the meniscus is partially removed. An intact meniscus may also be surgically “released” as a prophylactic measure against future injury (surgeon dependent). Next, a sterile suture is selected depending on the size, age, and activity level of the patient. The suture is passed around the fabella and through a tunnel created in the tibia. The suture is then tightened to stabilize the knee. See figure below. For larger patients, a suture can be placed on both the medial and lateral aspect of the knee.
Postoperative Care
Post-operative care after any extra-capsular stabilization includes activity restriction, incision care, physical therapy, and specific medications.
Activity Restriction – The post-operative recovery period usually lasts for about 8 weeks. During this period, the patient needs to have their activity restricted as to not cause complications with the stabilization. Too much activity can lead to implant failure, meniscal injury, and pain. We usually recommend confinement (crate, kennel, enclosure, small room), leash walks only, no jumping, no playing, no climbing, and no running for the majority of the recovery period. As the patient recovers, the surgeon will implement gradual return to normal activity.
Incision Care – It usually takes about 2-3 weeks for the incision and soft tissues to heal. During this time, it is important to monitor the incision for any excessive swelling, oozing, or incisional dehiscence (opening up). We also recommend an E-collar (cone) placed around the dogs’ head in order to keep them from chewing or licking at the incision. Licking or chewing at the incision can lead to dehiscence and/or infection of the site, which can be a serious complication especially if infection reaches the implant.
In addition, cold and/or warm compress may be implemented to decrease incisional swelling.
